The English language relies on comparative and superlative forms to describe qualities, compare people, objects, or ideas, and emphasize the degree of difference. Whether in academic writing, business communication, or everyday conversation, understanding how to use comparative and superlative adjectives correctly is essential. This guide provides detailed explanations, grammar rules, and practical examples to help learners master this important aspect of English grammar.
What Are Comparatives and Superlatives?
- Comparative: Used when comparing two people, things, or groups. It expresses a higher or lower degree of a quality.
- Example: This book is shorter than that one.
- Superlative: Used when comparing more than two items. It shows the highest or lowest degree of a quality.
- Example: She is the tallest student in the class.
In simple terms:
- Comparative = compares two.
- Superlative = compares three or more.
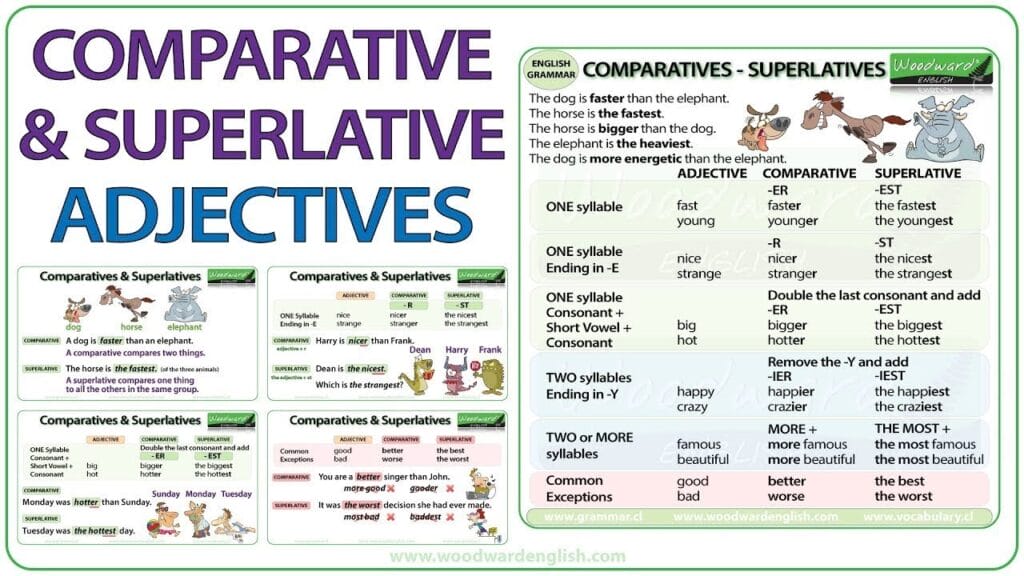
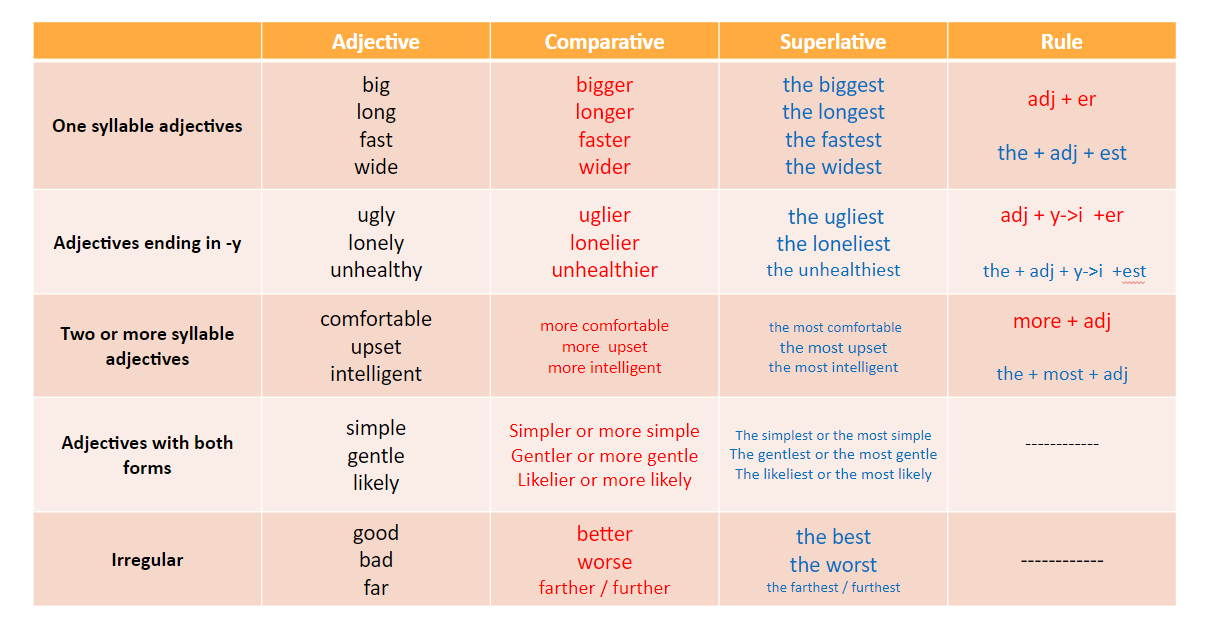
Formation Rules for Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
The form of the adjective changes depending on the word length and spelling. Below are the most common rules:
1. One-Syllable Adjectives
- Add –er for comparatives.
- Add –est for superlatives.
Examples:
- Tall → taller → tallest
- Small → smaller → smallest
- Fast → faster → fastest
2. One-Syllable Adjectives Ending in –e
- Just add –r for comparative.
- Add –st for superlative.
Examples:
- Large → larger → largest
- Wise → wiser → wisest

3. One-Syllable Adjectives Ending in a Single Consonant + Vowel + Consonant
- Double the final consonant before adding –er or –est.
Examples:
- Big → bigger → biggest
- Hot → hotter → hottest
- Sad → sadder → saddest
4. Two-Syllable Adjectives Ending in –y
- Change –y to –i before adding –er or –est.
Examples:
- Happy → happier → happiest
- Busy → busier → busiest
- Easy → easier → easiest
5. Two-Syllable and Longer Adjectives
- Use more for comparative and most for superlative.
Examples:
- Beautiful → more beautiful → most beautiful
- Expensive → more expensive → most expensive
- Comfortable → more comfortable → most comfortable
6. Irregular Adjectives
Some adjectives do not follow standard rules.
Examples:
- Good → better → best
- Bad → worse → worst
- Far → farther/further → farthest/furthest
- Little → less → least
- Many/much → more → most
How to Factor a Polynomial: A Complete Guide
Usage Rules and Sentence Structures
Understanding where and how to place comparatives and superlatives is essential for accuracy.
Comparatives in Sentences
Comparatives are usually followed by than.
Examples:
- This car is faster than that one.
- Today is colder than yesterday.
- My house is bigger than yours.
Superlatives in Sentences
Superlatives are usually preceded by the.
Examples:
- She is the tallest girl in the class.
- That was the most interesting movie I’ve seen.
- This is the least expensive option available.
Comparatives and Superlatives in Different Contexts
1. Academic Writing
- Comparative: Group A scored higher than Group B.
- Superlative: This method is the most effective approach in the study.
2. Business and Marketing
- Comparative: Our service is faster than the competition.
- Superlative: We provide the best customer support in the industry.
3. Everyday Conversation
- Comparative: Your phone is cheaper than mine.
- Superlative: This restaurant has the tastiest food in town.
Common Mistakes with Comparatives and Superlatives
- Using double forms
- ❌ More better
- ✅ Better
- Forgetting “the” with superlatives
- ❌ She is tallest in the class.
- ✅ She is the tallest in the class.
- Incorrect spelling changes
- ❌ Happy → happyer → happyest
- ✅ Happy → happier → happiest
- Mixing comparative with superlative meaning
- ❌ This is more easiest.
- ✅ This is the easiest.
Comparatives and Superlatives of Adverbs
Adverbs can also take comparative and superlative forms.
Short Adverbs (without –ly)
- Fast → faster → fastest
- Hard → harder → hardest
Long Adverbs (ending in –ly)
- Use more and most.
- Carefully → more carefully → most carefully
- Easily → more easily → most easily
Examples in sentences:
- He runs faster than his brother.
- She worked more carefully than her teammates.
- Among all the athletes, he ran the fastest.
Advanced Usage: Double Comparatives and Superlatives
Double Comparatives
Sometimes used to show a cause-and-effect relationship.
- The more you practice, the better you become.
- The harder you study, the higher your grades.
Double Superlatives (Avoid)
In formal English, double superlatives are incorrect.
- ❌ This is the most easiest exam.
- ✅ This is the easiest exam.
Comparatives and Superlatives in Idioms and Expressions
- No sooner said than done (comparative structure).
- The sooner, the better.
- At the very least.
- At best / at worst.
These expressions highlight how comparative and superlative forms enrich everyday English.
Teaching and Learning Tips
- Use visual comparisons
- Example: Show two pictures (a tall building vs. a short one). Ask learners: Which is taller?
- Practice with real-life examples
- Compare classmates, books, foods, or places.
- Create comparison charts
- Adjective → Comparative → Superlative table.
- Games and activities
- “Who is the tallest?” contest in class.
- “Find the most expensive item” activity online.
Quick Reference Table
| Adjective | Comparative | Superlative |
|---|---|---|
| Tall | Taller | Tallest |
| Happy | Happier | Happiest |
| Beautiful | More beautiful | Most beautiful |
| Good | Better | Best |
| Bad | Worse | Worst |
| Far | Farther/Further | Farthest/Furthest |
Why Mastering Comparatives and Superlatives Matters
- Clarity: Makes comparisons precise and understandable.
- Fluency: Improves writing and speaking skills.
- Persuasion: Important in marketing, debates, and negotiations.
- Accuracy: Prevents grammar mistakes that can confuse meaning.
Conclusion
The correct use of comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs is one of the building blocks of effective English communication. By following spelling rules, practicing sentence structures, and avoiding common mistakes, learners can achieve both fluency and accuracy. Whether writing academic essays, giving a business presentation, or having casual conversations, comparatives and superlatives make expression sharper and more powerful.
Master these forms, and your English will not only be clearer—it will also be better and perhaps even the best.